Hyperspectral inverse modeling
 Physics-informed models are important for understanding
the photon propagation through the tissue and the spectra
obtained in each pixel of the hyperspectral image.
Physics-informed models are important for understanding
the photon propagation through the tissue and the spectra
obtained in each pixel of the hyperspectral image.
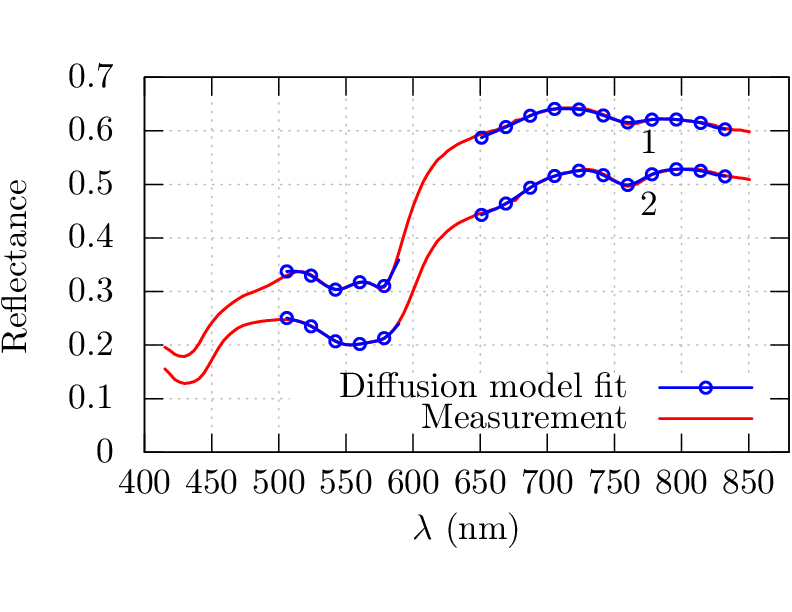
GPU-DM is an inverse model developed for estimating tissue constituents in each pixel of the hyperspectral image by employing a two-layered diffusion model. Essentially is each pixel labeled with physical information like oxygenation, blood volume fraction, melanin amount, water content or other physical properties in a depth-resolved way.
 The independent nature of the employed model enables
optimal GPU computing. Initialization of the model
is done using
The independent nature of the employed model enables
optimal GPU computing. Initialization of the model
is done using gpudm_initialize(), which sets the model
parameters according to a configuration file. A BIL-interleaved
reflectance line is uploaded to the GPU using gpudm_reinitialize().
The parameters are fitted using gpudm_fit_reflectance(). Derived
parameters can be downloaded to the host using gpudm_download_melanin(),
gpudm_download_530res() and gpudm_download700res(), into new BIL-interleaved
array with type of derived parameter along the band axis (oxyhemoglobin, deoxyhemoglobin, …).
For a complete example, see main.cpp.
The model is described in Bjorgan et al. (complete citation: Bjorgan, M. Milanic, L. L. Randeberg, “Estimation of skin optical parameters for real-time hyperspectral imaging applications”, J. Biomed. Opt. 19(6) (2014)). A description is also available in this technical report.